The appendix is a tiny pouch in the lower right abdomen. Although it may seem insignificant, inflammation of the appendix, known as appendicitis, can quickly turn into a medical emergency. While appendicitis can affect anyone, recognising appendix issues in women can be particularly tricky, as symptoms often mimic gynaecological or urinary tract problems.
Understanding how the appendix in female patients behaves, including its symptoms, causes, and treatment options, is crucial for early diagnosis and proper care. This blog will guide you through everything you need to know about appendix-related issues in women, with a special focus on which side appendix pain in females typically occurs, and how it can be misinterpreted.
What is the Appendix?
The appendix is a slender, tubular structure connected to the beginning of the large intestine, located in the lower right section of the abdomen. Although its exact function is still debated, it is believed to play a minor role in gut immunity.
In females, the appendix pain side is typically felt in the right lower abdomen. However, the pain may initially start near the belly button and move downward. What makes diagnosis in women more complex is that appendix pain can sometimes be confused with menstrual cramps, ovarian cysts, or other reproductive issues.

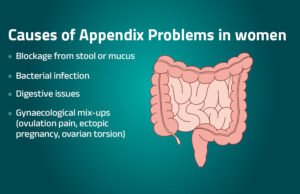
Causes of Appendix Problems in Females
The causes of appendix in female patients are generally the same as in men, but hormonal changes and reproductive anatomy can complicate diagnosis. Common causes include:
- Obstruction: A blockage in the appendix caused by stool, mucus, or parasites can lead to inflammation.
- Bacterial Infection: Once the appendix is blocked, bacteria can multiply rapidly, resulting in infection and swelling.
- Digestive Issues: Chronic digestive problems can contribute to appendix inflammation.
- Gynaecological Misdiagnosis: Women may experience right-sided pelvic pain due to ovulation, ectopic pregnancy, or ovarian torsion, which can be mistaken for appendicitis.
Due to these overlapping symptoms, understanding the root causes of appendix in female patients requires careful evaluation by a trained healthcare professional.
Common Symptoms of Appendix in Women
Recognising the symptoms of appendicitis in women patients often report can often help in early diagnosis. The tricky part is that symptoms in females are not always straightforward. They may be mistaken for urinary tract infections or reproductive system issues.
Key symptoms include:
- Lower right abdominal pain is often linked to appendix issues, especially in women.
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Pelvic or back pain
- Bloating or gas
- Fever and chills


The pain may worsen with movement, coughing, or pressing on the abdomen. For women, the pain may also radiate toward the pelvis, making it harder to distinguish from gynaecological problems.
Diagnosis Process
Diagnosing appendicitis in women can be more complicated than in men. Doctors must rule out conditions like:
- Ovarian cysts
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Endometriosis
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
To confirm the diagnosis, the following tests may be used:
- Physical Examination: Checking for tenderness in the right lower abdomen.
- Ultrasound or CT Scan: Helps visualize the inflamed appendix.
- Blood Tests: Look for signs of infection.
- Urine Test: To rule out urinary infections.
These steps help ensure accurate diagnosis, especially when the symptoms of appendicitis in women patients overlap with other conditions.
Treatment Options for Appendix in Women
Treatment depends on the severity of the condition. In most cases, surgical removal of the appendix, known as an appendectomy, is necessary.
- Medications: In rare, mild cases, antibiotics may be given to manage the infection.
- Female Appendicitis Surgery:
- Laparoscopic Appendectomy (minimally invasive) is often preferred for faster recovery and minimal scarring.
- Open Surgery is used in cases with complications like a ruptured appendix or widespread infection.
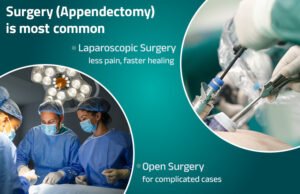
Female appendicitis surgery is generally safe and effective when performed promptly.
How Women Can Take Care After Appendix Treatment
Post-surgery recovery may differ slightly in women due to hormonal fluctuations, menstruation, or underlying gynaecological conditions. Some points to consider:
- Rest: Adequate rest for 1–2 weeks is usually required.
- Pain Management: Mild pain around the surgical site is normal and managed with medication.
- Avoid Strain: Heavy lifting or intense physical activity should be avoided.
- Menstrual Discomfort: Some women may notice changes in menstrual patterns temporarily.
Proper post-operative care ensures smooth healing and prevents complications like infections or adhesions.
When to See a Doctor
If you’re a woman experiencing:
- Persistent or severe right lower abdominal pain
- Nausea, vomiting, or fever
- Pain that worsens with movement
- Pelvic discomfort not related to menstruation
Seek medical attention immediately. Prompt medical evaluation and care are essential to avoid rupture and other severe complications.
Conclusion
The appendix in female patients can present unique diagnostic challenges due to overlapping symptoms with reproductive and urinary issues. However, understanding the warning signs, getting a timely evaluation, and undergoing proper treatment can ensure full recovery.
Whether you’re facing mild discomfort or intense pain in the lower right abdomen, don’t ignore it. Consult a qualified Gastro Surgeon in Ahmedabad, Dr. Varun Bajaj, to get an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
FAQs
Which side is the appendix pain in females?
In females, appendix-related pain often begins near the navel and gradually moves to the lower right side of the abdomen.
What are the early symptoms of appendicitis in women?
Early signs include abdominal pain (especially right side), nausea, loss of appetite, bloating, and low-grade fever. These symptoms of appendicitis in women patients can sometimes mimic other conditions.
What causes appendicitis in females?
The causes of appendix in female patients include blockage of the appendix, bacterial infection, and sometimes complications related to digestion or hormonal changes.
Is surgery always required for female appendicitis?
For most women, appendectomy is the standard and lasting treatment for appendicitis. However, in select mild cases, antibiotics may be used initially.
How long is the recovery after appendix surgery for women?
Recovery from a laparoscopic appendectomy usually takes 1–2 weeks, while open surgery may require a longer healing period. Hormonal factors or gynaecological issues may influence recovery time in some women.